Fix Facebook Can’t Log Out Issue
Have you ever experienced trouble logging out of Facebook?
Check Facebook Server Status
To check the Facebook Server Status, follow these steps:
1. Open your preferred web browser on your device.
2. Go to the official Facebook website.
3. Look for the “Help” or “Support” section on the website.
4. Click on the “Server Status” or “Service Status” option.
5. On the server status page, you will see the current status of Facebook’s servers.
6. If the servers are marked as “Up” or “Operational,” it means Facebook is running smoothly.
7. If the servers are marked as “Down” or “Degraded Performance,” it indicates there might be an issue.
8. If there is an ongoing issue, Facebook will usually provide updates and estimated time for resolution.
9. If the servers are running fine, but you still can’t log out of Facebook, try clearing your browser cache.
10. If the issue persists, consider rebooting your device and trying again.
11. If you’re using the Facebook mobile app, make sure it is up to date by checking for updates on the App Store or Google Play Store.
12. You can also try logging out and logging back in on a different device or using a different web browser.
13. If none of these steps work, it might be a temporary glitch or a software bug. In such cases, it’s best to contact Facebook support for further assistance.
Clear Cache and Cookies
To fix the Facebook can’t log out issue, one solution is to clear the cache and cookies on your device. This can help resolve any glitches or bugs that might be causing the problem. Here’s how to do it:
1. On your mobile app, open the Facebook app.
2. On Android, tap the three horizontal lines in the top right corner, then scroll down and tap “Settings & Privacy.” On iPhone, tap the three horizontal lines in the bottom right corner, then scroll down and tap “Settings & Privacy.”
3. Tap “Settings.”
4. Scroll down and tap “Clear Cache and Cookies.”
5. A confirmation message will appear. Tap “Clear” to proceed.
6. Once the cache and cookies are cleared, try logging out of Facebook again and see if the issue is resolved.
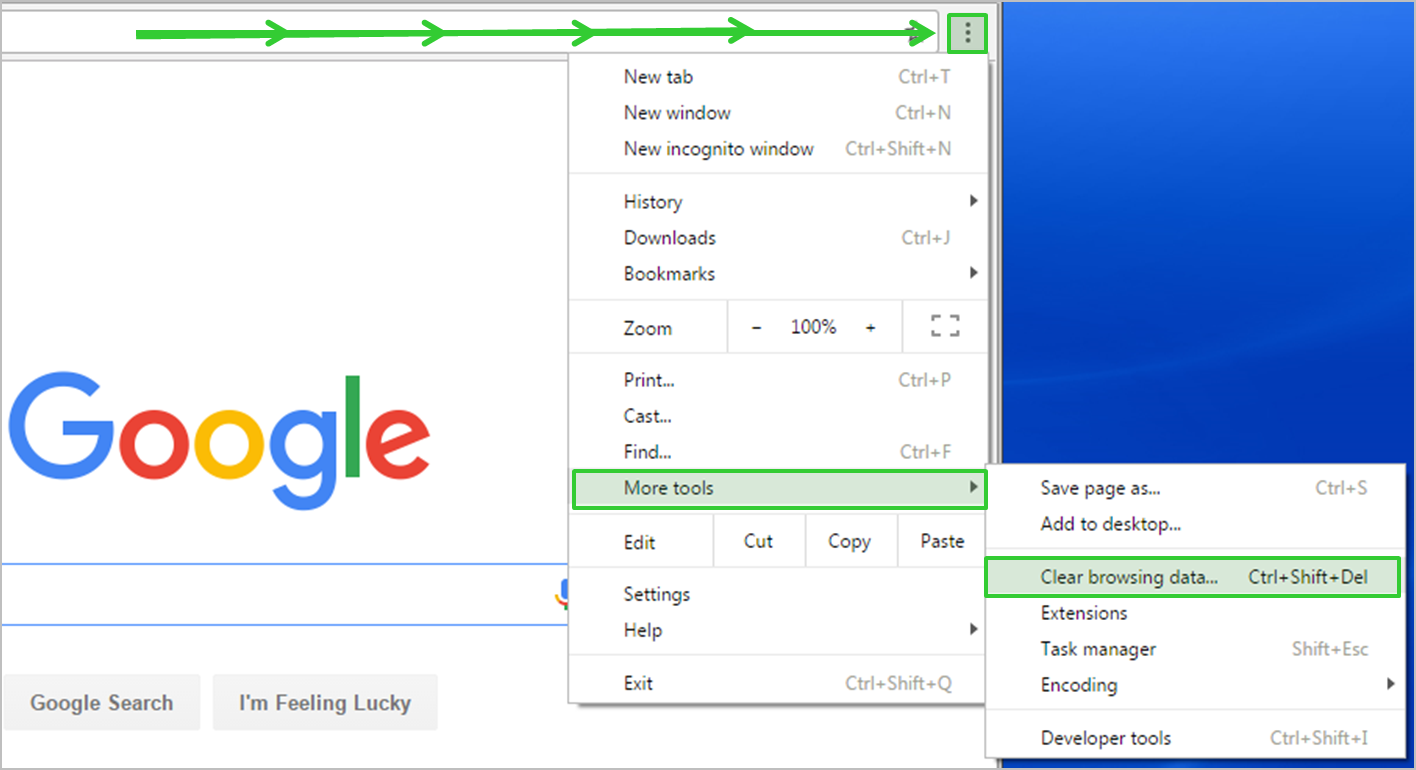
Clearing the cache and cookies can also be done on the Facebook website. Here’s how:
1. Open your internet browser and go to the Facebook website.
2. On Microsoft Windows, press Ctrl+Shift+Delete on your keyboard. On Mac, press Command+Shift+Delete.
3. A window will appear with options to clear browsing data. Make sure “Cache” and “Cookies” are selected.
4. Click “Clear” or “Delete” to proceed.
5. Once the cache and cookies are cleared, try logging out of Facebook again and see if the issue is resolved.
Check Internet Connection
To fix the Facebook can’t log out issue, the first step is to check your internet connection. Make sure you are connected to a stable and reliable network. If you’re using Wi-Fi, ensure that you have a strong signal and try restarting your router if necessary. If you’re using mobile data, check if you have a stable connection and consider switching to a different network if needed.
If your internet connection is fine, try clearing your browser cache and cookies. This can help resolve any glitches or conflicts that may be causing the log out issue.
If you’re using a mobile device, try closing the Facebook app completely and reopening it. You can also try restarting your device to refresh the system.
If the issue persists, try using a different browser or device to log out of Facebook. Sometimes, software bugs or compatibility issues can cause login problems on specific platforms.
Disable Browser Extensions
1. In your browser, locate the menu button (usually represented by three dots or lines) and click on it.
2. From the dropdown menu, select “Extensions” or “Add-ons.”
3. You will be directed to a page that lists all the extensions installed in your browser.
4. Find the extension that may be causing the issue. This could be any extension related to Facebook or social media in general.
5. Once you’ve identified the extension, click on the toggle or checkbox next to it to disable it.
6. After disabling the extension, try logging out of Facebook again to see if the issue has been resolved.
If disabling the extensions doesn’t solve the problem, you can also try clearing your browser cache and cookies. This can help eliminate any temporary data that may be causing the issue.
By addressing the causes of freezing programs and damaged DLL files, Fortect can help ensure that Windows and other programs run smoothly. It can also repair the causes of Blue Screen of Death (BSoD) errors and assist with OS recovery without affecting user data.
Log Out of All Devices
1. Open your Facebook account on a computer or mobile browser.
2. Click on the downward-facing arrow in the top-right corner of the screen to open the drop-down menu.
3. Select “Settings & Privacy” and then click on “Settings”.
4. On the left-hand side, click on “Security and Login”.
5. Under the “Where You’re Logged In” section, you’ll see a list of devices where you’re currently logged in.
6. Click on the three dots next to each device and select “Log out” to sign out of that specific device.
7. If you want to log out of all devices at once, click on the “Log out of all sessions” button at the top-right corner of the page.
8. Confirm your decision by clicking “Log Out” in the pop-up window.
Restart Your Device
Restarting your device is a simple yet effective solution for fixing the “Facebook can’t log out” issue. To do this on an Android device, press and hold the power button until the power menu appears. Then, select “Restart” and wait for your device to reboot. On an iPhone, press and hold the power button (or the volume up/down buttons together) until the power slider appears. Slide it to power off, and then turn your device back on.
Restarting your device can resolve various technical glitches, including issues with Facebook not allowing you to log out. By rebooting your device, you clear the cache, close any background processes, and refresh the device’s system. This can help eliminate any software bugs or server-related problems that may be causing the log out issue.
If you’re still unable to log out after restarting, you can try clearing the cache and data of the Facebook app. To do this on an Android device, go to “Settings,” then “Apps” or “Applications,” and find the Facebook app. Tap on it, then select “Storage.” From there, tap on “Clear cache” and “Clear data” to remove any temporary files or stored login information. On an iPhone, go to “Settings,” then “General,” and select “iPhone Storage.” Find the Facebook app and tap on it, then choose “Offload App” or “Delete App.” Afterward, reinstall the app from the App Store.
Update Facebook App
![]()
To update the Facebook app and fix the “can’t log out” issue, follow these steps:
1. Open the Facebook app on your mobile phone or tablet.
2. Go to the settings menu. This can usually be found by tapping on the three horizontal lines in the top-right corner of the screen.
3. Scroll down and select “App Settings” or “Account Settings,” depending on your device.
4. Look for the option to update the app. It may be labeled as “Check for Updates” or “Update App.”
5. Tap on this option, and the app will check for any available updates. If an update is available, follow the prompts to download and install it.
6. Once the update is complete, try logging out of Facebook again to see if the issue has been resolved.
If you’re still experiencing problems, try clearing the cache and data of the Facebook app. Here’s how:
1. Go to the settings menu of your device.
2. Find the “Apps” or “Applications” section.
3. Look for the Facebook app and tap on it.
4. Select “Storage” or “Storage & Cache” (depending on your device).
5. Tap on “Clear Cache” and “Clear Data” to remove any temporary files and settings associated with the app.
6. Restart your device and try logging out of Facebook again.
If these steps don’t solve the problem, you may need to uninstall and reinstall the Facebook app. Here’s how:
1. Go to the settings menu of your device.
2. Find the “Apps” or “Applications” section.
3. Look for the Facebook app and tap on it.
4. Select “Uninstall” or “Uninstall Updates” to remove the app from your device.
5. Go to the app store (Google Play Store for Android or App Store for iOS) and search for “Facebook.”
6. Download and install the app again.
7. Open the app, log in, and try logging out to see if the issue has been resolved.
If you’re still unable to log out of Facebook, it may be a temporary glitch or an issue with your device’s software. Consider restarting your device or contacting Facebook support for further assistance.
Force Stop Facebook Mobile App
To force stop the Facebook mobile app, follow these steps:
1. On your Android device, go to the Settings menu.
2. Scroll down and tap on “Apps” or “Applications”.
3. Look for the Facebook app and tap on it.
4. Tap on “Force Stop” to close the app completely.
5. Confirm the action if prompted.
6. Once the app is force stopped, you can try logging out of Facebook again.
If you’re still experiencing issues with logging out, you can also try clearing the cache of the Facebook app:
1. Go to the Settings menu on your Android device.
2. Tap on “Apps” or “Applications”.
3. Find the Facebook app and tap on it.
4. Tap on “Storage” or “Storage & cache”.
5. Tap on “Clear cache” to delete the temporary data.
6. Try logging out of Facebook again.
If the issue persists, you may need to uninstall and reinstall the Facebook app or check for any available updates. Remember to restart your device after performing any of these steps.
These instructions should help you resolve the Facebook can’t log out issue on your Android device.
Wait for Facebook to Fix the Issue
To fix the Facebook can’t log out issue, the best course of action is to wait for Facebook to address the problem. Facebook is aware of the issue and is actively working on a solution. In the meantime, there are a few steps you can take to alleviate the problem. First, try clearing your browser cache and cookies.
This can help refresh your session and potentially resolve any temporary glitches. If that doesn’t work, you can try logging out from a different device or browser. Sometimes, the issue may be specific to a certain device or browser configuration. Additionally, make sure you’re using the latest version of the Facebook app or accessing Facebook from a supported browser.
FAQs
How can I force log out of Facebook?
To force log out of Facebook, you can go to Settings in the top right corner of Facebook. From there, scroll down to Security and Login. Look for the WHERE YOU’RE LOGGED IN section and tap on it. If needed, tap See More to view all logged-in sessions. Locate the session you wish to end and tap on it, then select Log out.
Why is my Facebook not letting me log in?
Your Facebook may not be letting you log in due to various reasons such as forgetting your login details, account hacking, Facebook bugs, cache or cookie problems, browser issues, malware/virus infection, or if your account has been disabled by Facebook.
How do I log everyone out of Facebook?
To log everyone out of Facebook, go to the Security and login settings page and click on “See more” under the “Where you’re logged in” section. Then, at the bottom of the list of sessions, choose “Log Out Of All Sessions.” Confirm the log out action by clicking “Log Out” in the dialogue box.
I encountered an issue with Facebook where it wouldn’t allow me to log out, causing some inconvenience. Download this tool to run a scan






