Introduction to Selenium? – User friendly Tech help
Today we are focusing on the background check of Selenium.
n
nWhat is Selenium?
n
nSelenium automates browsers.Selenium is an Open Source(Freely Available)and combination of software tools which is used in automation testing of web applications across different browsers and platforms.
n
nSelenium is a set of multifarious software tools each with a different approach to supporting test automation.
n
The name Selenium comes from a joke made by Jason Huggins(Inventor of Selenium) in an email, mocking a competitor named Mercury(UFT now), saying that you can cure mercury poisoning by taking selenium supplements.
n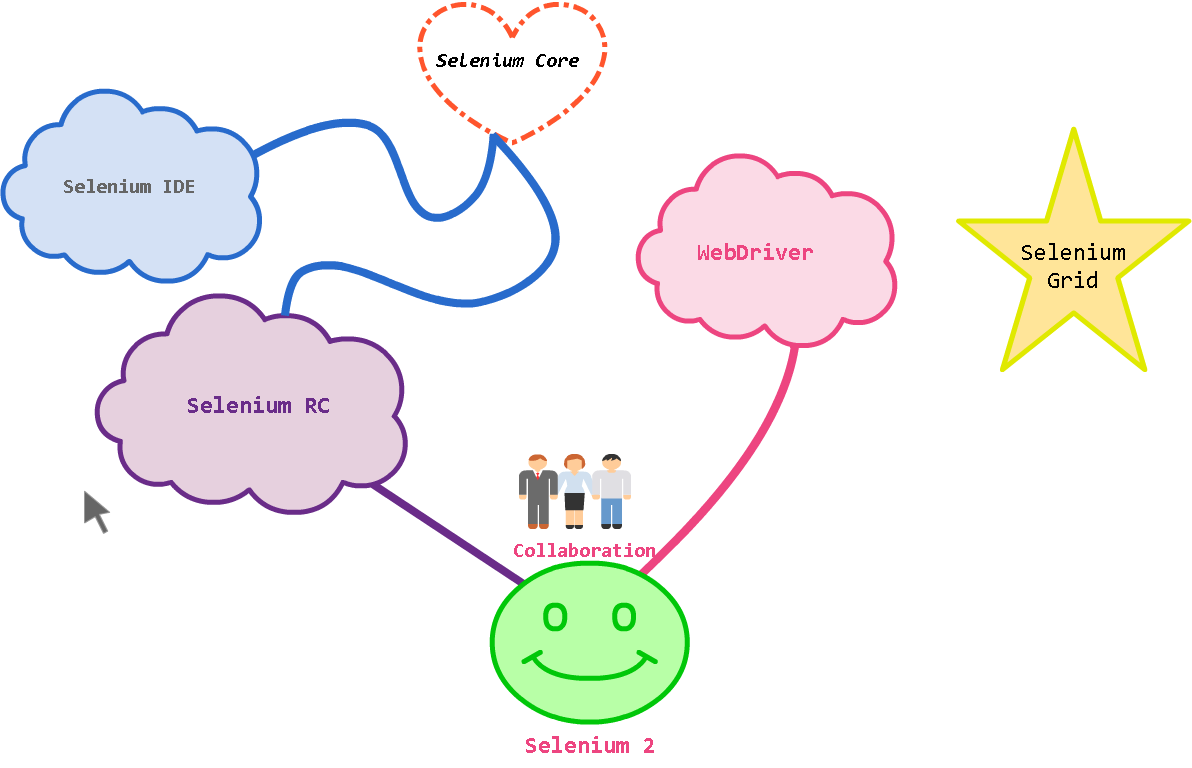
nIt consists of 4 components:-
n
n• Selenium IDE( Integrated Development Environment)
n• Selenium RC( Remote Control)
n• WebDriver
n• Selenium Grid
n
nWhat about the History?
n
n
n
nInvented in 2004, by Jason Huggins,while testing an internal application(Time and Expenses (T&E) system) at ThoughtWorks. In order to avoid the frequent manual testing on different browsers , he created a Javascript library to imitate user actions .This javascript library originally called “Selenium” but later referred to as “Selenium Core” which underlies all the functionality of Selenium Remote Control (RC) and Selenium IDE.
n
nInterview with Jason Huggins
n
Note:- Selenium core comes with limitation that being written in pure Javascript, its initial design required developers to host Core and their tests on the same server as the application under test (AUT) in order to avoid browser’s security policies and the Javascript sandbox.
n
nSeleniumRC/Selenium 1
n
To overcome the same origin policy issue(where a browser won’t allow JavaScript to make calls to anything other than the server from which the current page has been served) an HTTP proxy was written so that every HTTP request could be intercepted by Selenium. This resulted in selenium bindings in multiple languages, because the language bindings were controlling the browser at a distance, it results in the invention so was called “Selenium Remote Control”, or “Selenium RC”. Credit for this goes to Jason and Paul hammant.
n
nSelenium IDE
n
It’s credit goes to Shinya Kasatani (@shinya), from Japan created a Firefox plugin that effectively wrapped the “core” code into an IDE that would allow record, edit and playback of Selenium scripts).
n
nSelenium Webdriver
n
Webdriver,Inventor was Simon Stewart (a ThoughtWorks consultant in Australia at that time,now as off 2014 , part of Facebook team ) started “WebDriver” in early 2007, who in order to overcome the limitation of separate server to be started in RC , created an approach so that tool can speak directly to browser using the native methods of browser and operating system.
n
nRC v/s WebDriverWhen WebDriver was released there were significant differences between it and Selenium RC,most prominent was:-
nOperation Level:-
nOne of operational difference was RC drives the browser from within the browser (using Selenium core Javascript) and all events that were performed on the application under test (AUT), was passed through this core.This JavaScript Library was generic in nature and not specific to any browser, which made script to behave abnormally on some browsers. Contrary to this WebDriver handles the browser from outside , as it contains the implementation for each browser (WebDriver Interface like FireForxDriver,IEDriver,ChromeDriver),This provides test script to have better control on the browser as WebDriver implementation speaks to the browser in its native language.
nBetter API’s :-
nSelenium RC had a dictionary-based API(with all methods exposed as single class) while webdriver had a more object-oriented API.
nTesting Mobile Application:-
n
nWe can test mobile based applications by using mobile drivers like IPhoneDriver and AndroidDriver.
n
Selenium Grid
n
nThoughtWorker Philippe Hanrigou (@ph7) created ‘Selenium Grid’ which allowed Selenium RC to be used in expanded capacity. Selenium-Grid allows to execute tests on different machines against different browsers in parallel. Meaning, running of multiple tests at the same time against different machines running different browsers and operating systems.
nThis included the potential for multi-threading tests in parallel from a single test invocation, and utilizing a large number of browser (multi-OS) elsewhere
n
Selenium 2
nIt was only In August, 2009, it was announced that the two projects would merge, thus RC+ Webdriver came as Selenium WebDriver.Thus overcoming the limitations of RC and also utilizing the capabilities of RC(different lanugauge binding), selenium webdriver was formed (Also called Selenium2)
n
nSelenium 1.0 + WebDriver = Selenium 2.0
n
nStarting with Selenium
n
